“The Importance of Gut Health: How Your Digestive System Impacts Overall Wellness”
What is gut health?
Gut refers to entire digestive system and gut health is described as the balance functioning of the digestive system. The physical structure of the gut from mouth to colon is intact and functioning properly. It is digesting and absorbing nutrients well with regular and healthy bowl movements. Microbiome balance is present in the gut. Gut microbiome plays a crucial role in aiding digestion. these microbiomes help in production of essential nutrients and compounds.
The gut directly influences the following connected systems:
- Immune system (70-80% of immune cells are in the gut)
- Mental health through the gut-brain axis
- Hormone regulation
- Inflammation levels throughout the body
- Energy production and metabolism
Understanding the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome refers to the trillions of microorganisms that live in the digestive system. It is estimated to be 100 trillion microorganisms with 1000 different species of bacteria. It not only contains the bacteria but also contains the fungi, viruses, and other microorganisms. it is unique in each person just like fingerprint. A healthy microbiome has high biodiversity.
Key Functions:
1. Digestion and Nutrient Processing
What is the gut microbiome and why is it important? Gut microbiomes are involved in breaking down of complex carbohydrates and helps on absorption of minerals. They produce essential vitamins like B12 and vitamin K. It metabolizes proteins and creates short-chain fatty acids. Learn more from Harvard Health.
2. Protective Functions
Gut microbiome trains the immune system to fight off against the pathogenic bacteria. It maintains the gut wall integrity by forming a barrier against harmful bacteria. Read more from NIH.
3. Communication Role
Gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters that involves in communication with the brain. It influences hormone production which affects appetite and satiety and have a significant impact on mood and behavior of the individual.
4. Gut Health and Immune System Regulation
The gut is home to around 70% of the immune system, where helpful bacteria assist in distinguishing between hazardous invaders and safe compounds.
5. Gut Health and Weight Loss Connection
Your metabolism and weight are greatly affected by the bacteria that live in your gut. Research published in science has shown that different combinations of bacteria can have an impact on:
- The number of calories you get from food
- The storage and distribution of fat
- Regulating blood sugar
- The levels of cholesterol
- The amount of energy used
Studies have demonstrated that people who have a more diversified gut microbiota are more likely to have a healthy weight and a better metabolic profile than those whose gut microbiomes are less diverse.

The Gut-Brain Connection
The “gut-brain axis,” which refers to the close relationship between the gut and the brain, is one of the most interesting discoveries made in recent years. According to research published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine, your stomach produces more than 90% of the serotonin in your body. Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is important for regulating mood and maintaining emotional well-being.
The enteric nervous system, which is sometimes called the “second brain,” is a neuronal network that is located in your digestive system. This system interacts with your brain through the vagus nerve, which affects:
- Emotions and moods
- Responses to stress
- Patterns of sleep
- The ability to think
- Levels of anxiety
Signs of Poor Gut Health
It is important to be able to identify the symptoms of poor gut health in order to preserve overall wellness. Some such markers are:
- Discomfort in the digestive system (such as bloating, gas, constipation, or diarrhea)
- Weight fluctuations that cannot be explained
- Long-term exhaustion
- Skin issues (acne, eczema)
- Food intolerances
- Infections that happen often
- Mood problems
- Problems with sleep
The Future of Gut Health
New linkages between gut health and several elements of human health are being discovered by ongoing research. Researchers are investigating:
- Nutrition that is tailored to the microbiota profiles of each person
- New treatment methods for different illnesses
- The microbiome’s impact on aging and lifespan
- The relationship between intestinal health and chronic disorders
- New probiotic and prebiotic therapies
How to improve gut health naturally
Maintaining a balanced gut microbiome is crucial for long-term health. Here are some practical ways for repairing an unhealthy gut and maintaining good gut health and wellness.
1. Eat a Diverse, Fiber-Rich Diet
Eat whole grains, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, which include prebiotic fiber that nourishes helpful bacteria. Learn about fiber from the Mayo Clinic.
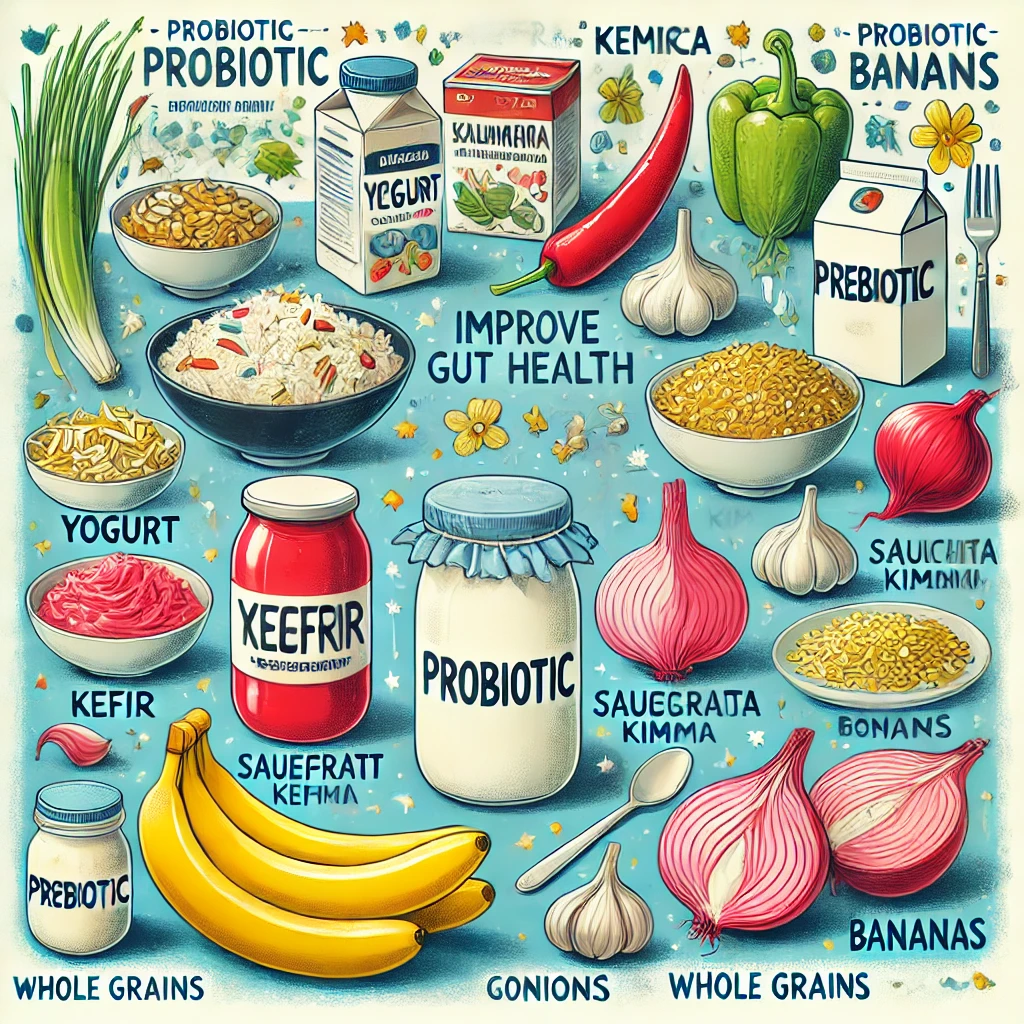
Include fermented foods in your diet, such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and miso, which are rich in probiotics and promote a healthy gut.
2. Stay Hydrated
Drinking enough water helps with digestion, the absorption of nutrients, and the mucosal lining of the intestines. More on hydration from CDC.
3. Manage Stress Effectively
Meditation, deep breathing, yoga, and regular exercise are all practices that can help control stress hormones that affect gut health. Read more on stress and digestion from Johns Hopkins.
4. Use Antibiotics Only When Necessary
Antibiotics can kill off good bacteria if you take them too often, so only take them when your doctor tells you to and think about taking probiotics afterward. More on antibiotic use from the CDC.
Conclusion
A healthy gut is essential for overall wellness, since it affects digestion, immunity, metabolism, and even mental health. You may improve your gut microbiome and general health by making intentional choices about your lifestyle, such as eating a balanced diet, reducing stress, and maintaining a regular sleep schedule. If you focus on your gut health and wellness today, you may experience long-term benefits, such as a lower risk of chronic diseases and a higher quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the best foods for gut health?
Foods for a healthy gut include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, garlic, onions, bananas, and whole grains, all rich in probiotics and prebiotics.
2. How long does it take to improve gut health?
Depending on diet and lifestyle changes, noticeable improvements can occur within a few weeks to a few months.
3. Can gut health improve mental health?
Yes, the gut-brain connection plays a role in mental health. An imbalanced microbiome can contribute to mood disorders, anxiety, and depression.
4. What are the best probiotics for gut health?
Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains are among the most beneficial probiotics for gut health.
5. How does gut health affect your immune system?
A healthy gut supports immune function by regulating inflammation and preventing harmful bacteria from taking over.
Investing in gut health and wellness today can have profound benefits for your future well-being!